In relational databases, columns in one table often relate to columns in other tables through associations. Relational database design aims to minimize redundant data, which can cause several issues:
- Unnecessary consumption of storage space
- Inconsistencies and conflicts in stored data due to duplication
- Compromised data integrity
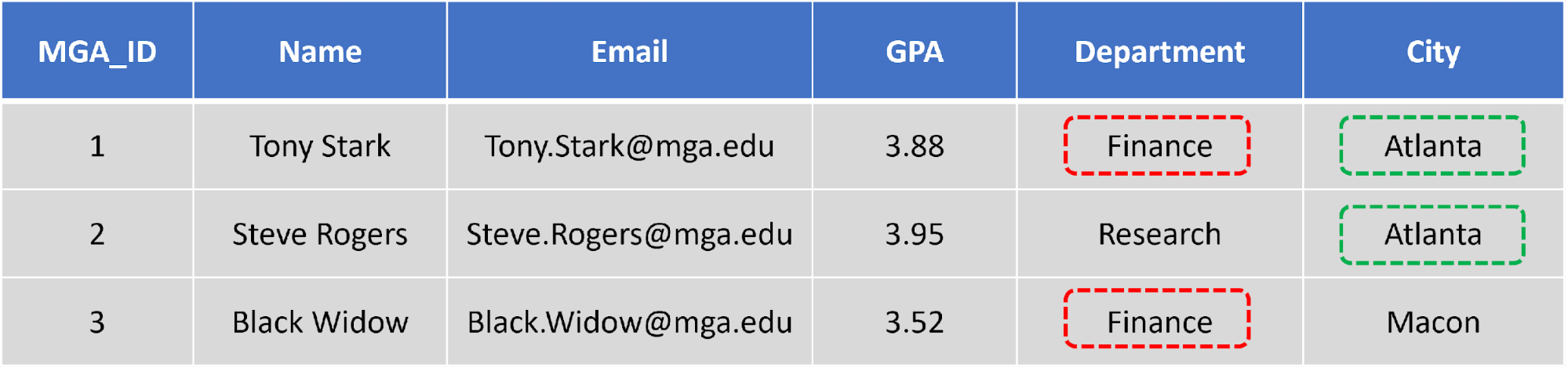
| MGA_ID | Name | GPA | Department | City | |
|
1 |
Tony Stark | Tony.start@mga.edu | 3.88 | Finance | Atlanta |
| 2 | Steve Rogers | Steve.Rogers@mga.edu | 3.95 | Research | Atlanta |
| 3 | Black Widow | Black.Widow@mga.edu | 3.52 | Finance | Macon |
In this table, "Finance" and "Atlanta" are replicated.
In a relational design, data would be divided into multiple tables such as Department, Student, and Location table.
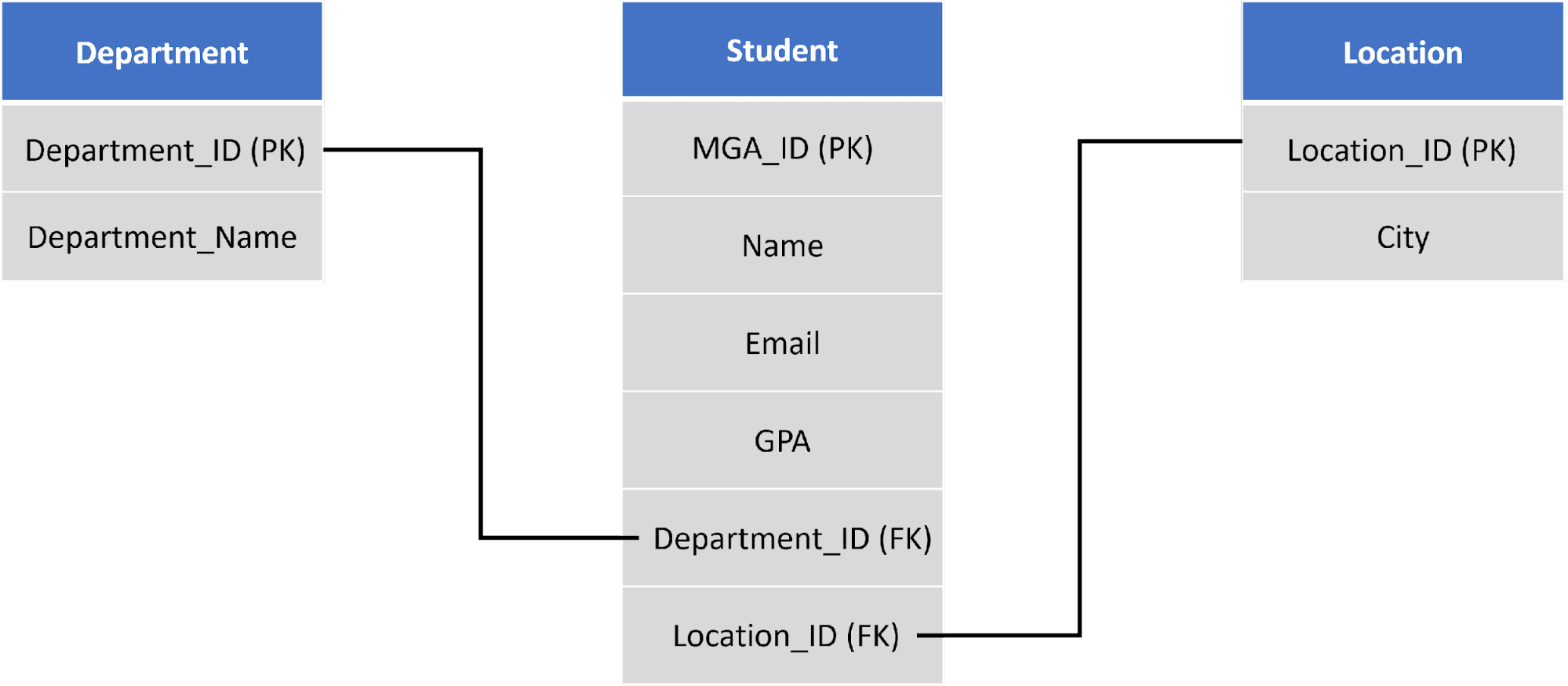
A foreign key (FK) is a column within one table that refers to the primary key in another table.
The following SQL statements are used to create the Department and Location tables:
| CREATE TABLE Department(Department_ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, Department_Name TEXT) CREATE TABLE Location(Location_ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, City TEXT) |
When creating the Student table, we utilize the FOREIGN KEY table constraint to designate the foreign keys:
| CREATE TABLE Student(MGA_ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, Name TEXT, Email TEXT, GPA REAL, Department_ID INTEGER, Location_ID INTEGER, FOREIGN KEY(Department_ID) REFERENCES Department(Department_ID), FOREIGN KEY(Location_ID) REFERENCES Location(Location_ID)) |