To write to an existing file in Python, you can use the open() function with specific modes. The two most common modes for writing are:
- Append Mode ("a"): Appends content to the end of the file without removing the existing content.
- Write Mode ("w"): Overwrites any existing content in the file.
Example: Appending to a File
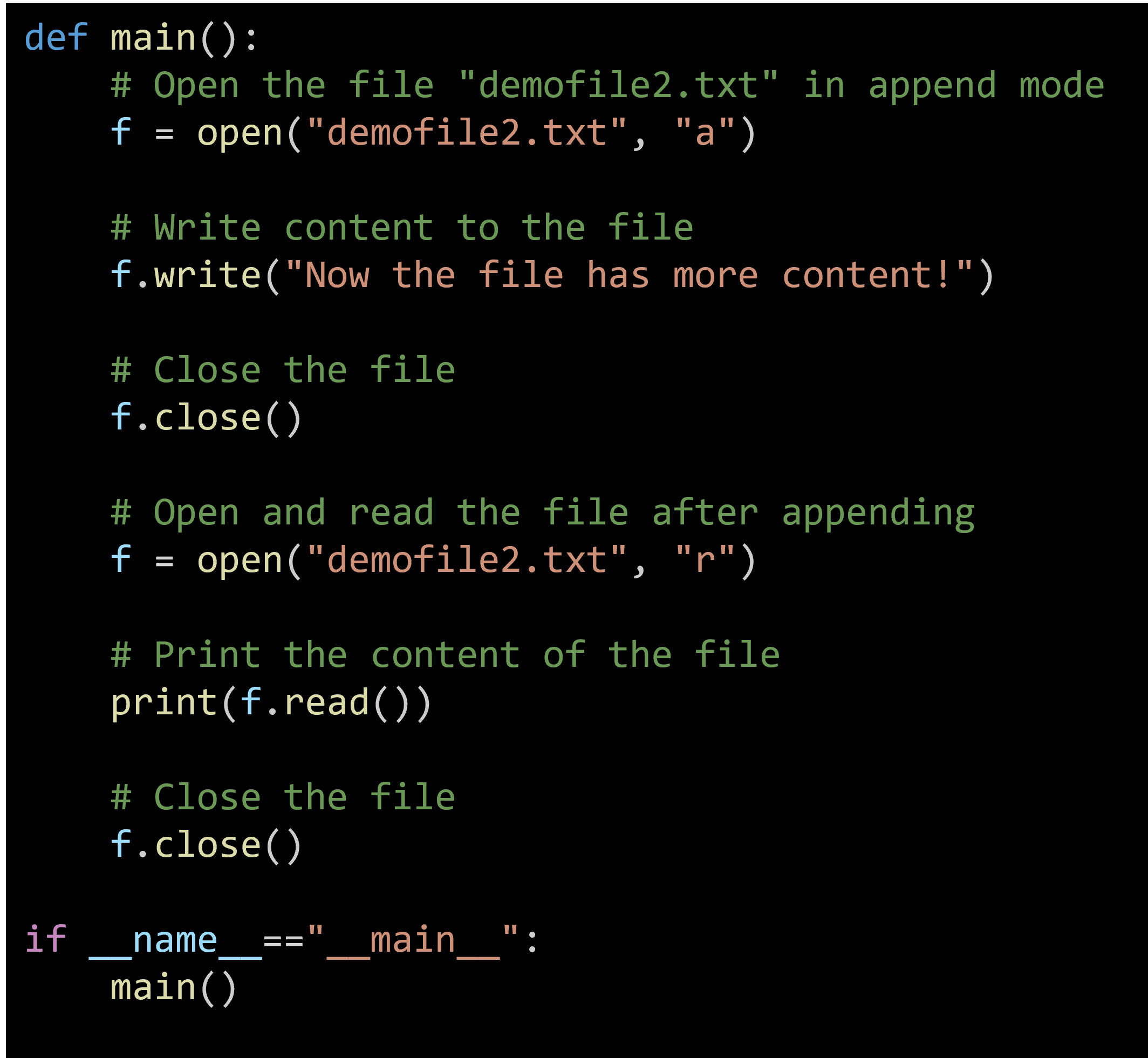
Here's an example of how to append content to an existing file:
Explanation:
- Open the File in Append Mode: Use open("demofile2.txt", "a") to open the file in append mode.
- Write to the File: The write() method appends the specified string to the end of the file.
- Close the File: Always close the file after writing to ensure all changes are saved and resources are freed.
- Read and Print the File: Reopen the file in read mode and print its content to verify that the new content has been appended.
Example: Overwriting a File
If you want to overwrite the existing content, you can use write mode ("w") instead:

Explanation:
- Open the File in Write Mode: Use open("demofile2.txt", "w") to open the file in write mode.
- Write to the File: The write() method overwrites any existing content with the specified string.
- Close the File: Always close the file after writing to ensure all changes are saved and resources are freed.
- Read and Print the File: Reopen the file in read mode and print its content to verify that the old content has been overwritten.
Best Practices
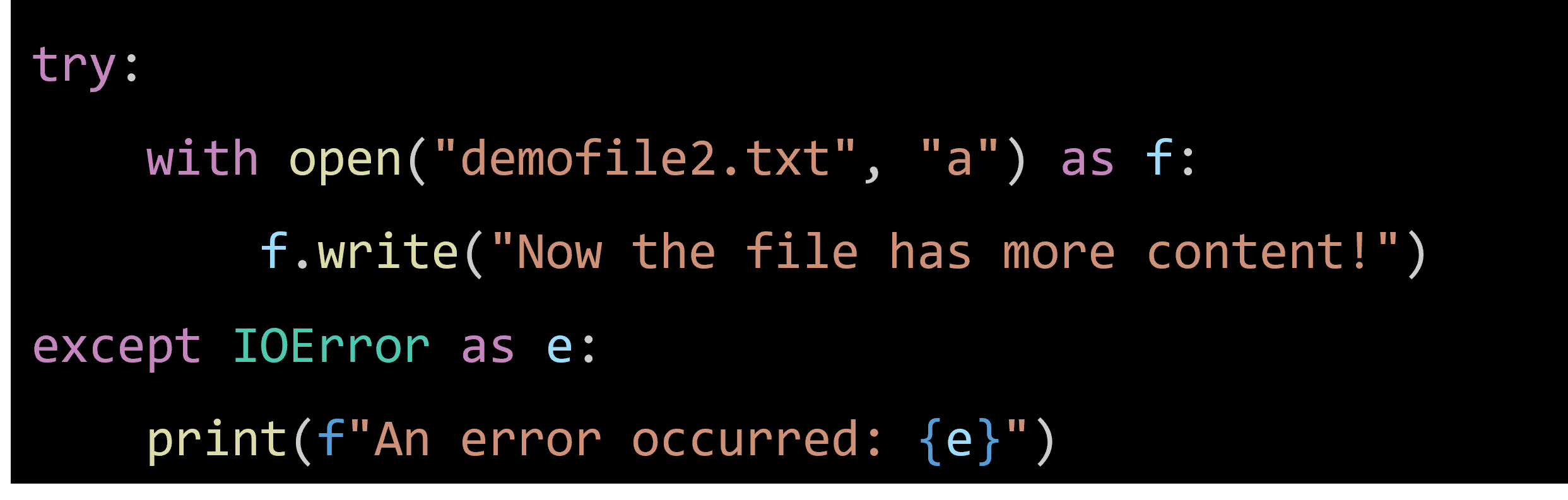
- Use with Statement: Using the with statement ensures that files are properly closed after their suite finishes, even if an exception is raised.
|
with open("demofile2.txt", "a") as f: |
- Error Handling: Handle potential errors such as file not found or permission issues using try-except blocks.