Design is the most important part of the program development cycle
- Program design serves as the blueprint for the entire development process. A well-thought-out design ensures that the program:
- Meets the user’s needs
- Is logically organized and maintainable
- Can be developed efficiently with fewer bugs
Understand the task that the program is to perform
- Work with the customer to understand the program’s purpose
- What is the program’s goal?
- What problem is it trying to solve?
- Who will use it and how?
- Ask questions about program details
- What are the inputs and expected outputs?
- Are there any rules or constraints?
- What should the program do in case of errors?
Determine the steps that must be taken to perform the task
- Break down the required task into a series of steps
- Decompose the problem into smaller, manageable parts. Think logically about the flow of data and actions the program needs to perform.
- Create an algorithm
- An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem or performing a task. It outlines the logical flow of the program before any code is written. Think of it as a detailed recipe or a roadmap to the solution.
Algorithm: A set of well-defined logical steps that must be taken to perform a task
- An algorithm:
- Is a precise and ordered list of actions
- Must be unambiguous and follow logical reasoning
- Should eventually lead to a result or output
- For example, an algorithm to calculate the average of three numbers might be:
- Get three numbers from the user
- Add the numbers together
- Divide the total by 3
- Display the result
- A good algorithm leads to an efficient, understandable, and reliable program.
Pseudocode
- "Fake code" used to model a program before coding
- Pseudocode is a simplified, informal way of describing a program’s logic using plain language mixed with programming-like structures.
- It looks like code but doesn’t follow any specific programming language syntax.
- That’s why it’s often called "fake code."
- Key Characteristics of Pseudocode
- Informal language that has no syntax rules
- Not meant to be compiled or executed
- Used to create a model of a program

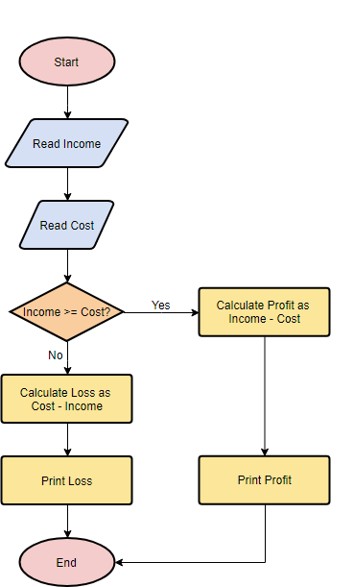
Flowchart
- A Visual Representation of a Program's Logic
- A flowchart is a diagram that shows the step-by-step flow of a program using standard symbols.
- It provides a graphical overview of how a program or process operates, helping to visualize the logic before writing code.