A "graph" in mathematics and computer science consists of "nodes", also known as "vertices". Nodes may or may not be connected with one another. In our illustration, Figure 1, - which is a pictorial representation of a graph,
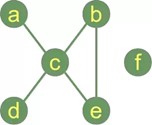
Figure 1. Graphs and its components.
- The node "a" is connected with the node "c", but "a" is not connected with "b". The connecting line between two nodes is called an edge. If the edges between the nodes are undirected, the graph is called an undirected graph. If an edge is directed from one vertex (node) to another, a graph is called a directed graph. An directed edge is called an arc. Though graphs may look very theoretical, many practical problems can be represented by graphs. They are often used to model problems or situations in physics, biology, psychology and above all in computer science. In computer science, graphs are used to represent networks of communication, data organization, computational devices, the flow of computation, In the latter case, the are used to represent the data organization, like the file system of an operating system, or communication networks. The link structure of websites can be seen as a graph as well, i.e. a directed graph, because a link is a directed edge or an arc. Python has no built-in data type or class for graphs, but it is easy to implement them in Python. One data type is ideal for representing graphs in Python, i.e. dictionaries. The graph in our illustration can be implemented in the following way:
|
graph = { "a" : {"c"}, |
The keys of the dictionary above are the nodes of our graph. The corresponding values are sets with the nodes, which are connected by an edge. A set is better than a list or a tuple, because this way, we can have only one edge between two nodes. There is no simpler and more elegant way to represent a graph.
An edge can also be ideally implemented as a set with two elements, i.e. the end nodes. This is ideal for undirected graphs. For directed graphs we would prefer lists or tuples to implement edges.
Function to generate the list of all edges:
Output:
![]()
As we can see, there is no edge containing the node "f". "f" is an isolated node of our graph. The following Python function calculates the isolated nodes of a given graph:
Output:
![]()