In a standard queue described in the previous section, elements are managed on a First-In, First-Out basis, where they are added to the back and removed from the front.
However, a priority queue assigns priority levels to its elements. When accessing elements, those with the highest priority are dealt with first, reflecting a largest-in, first-out behavior. For instance, in a hospital's emergency room, in a hospital's emergency room, patients are prioritized with numbers, ensuring that the most urgent cases receive immediate attention.
- How it works?
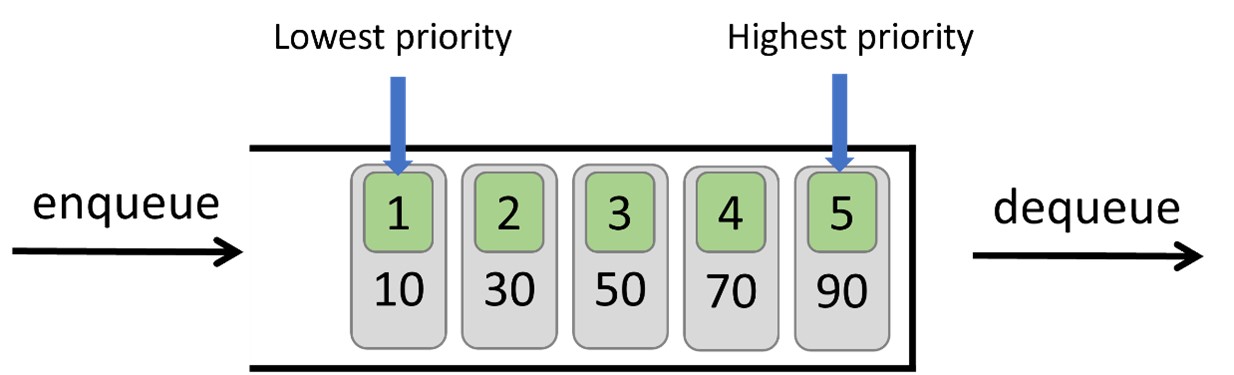
The item with the highest priority is positioned at the forefront to be served first.
- Priority Queue Implementation
Using a List:
Let's suppose that 4 represents the highest priority, while 1 signifies the lowest priority.
Output:
|
Size of queue: 4 Is queue empty? False Dequeue: (4, 'Jane') Dequeue: (3, 'Tom') Dequeue: (2, 'John') Dequeue: (1, 'Kelly') Is queue empty? True |
Using a heapq:
Let's suppose that 4 represents the highest priority, while 1 signifies the lowest priority.
Output:
|
Size of queue: 4 Is queue empty? False Dequeue: Jane Dequeue: Tom Dequeue: John Dequeue: Kelly Is queue empty? True |
Using a PriorityQueue:
In this scenario, let's designate 4 as the highest priority and 1 as the lowest priority.
Output:
|
Size of queue: 4 Is queue empty? False Dequeue: Jane Dequeue: Tom Dequeue: John Dequeue: Kelly Is queue empty? True |